外观
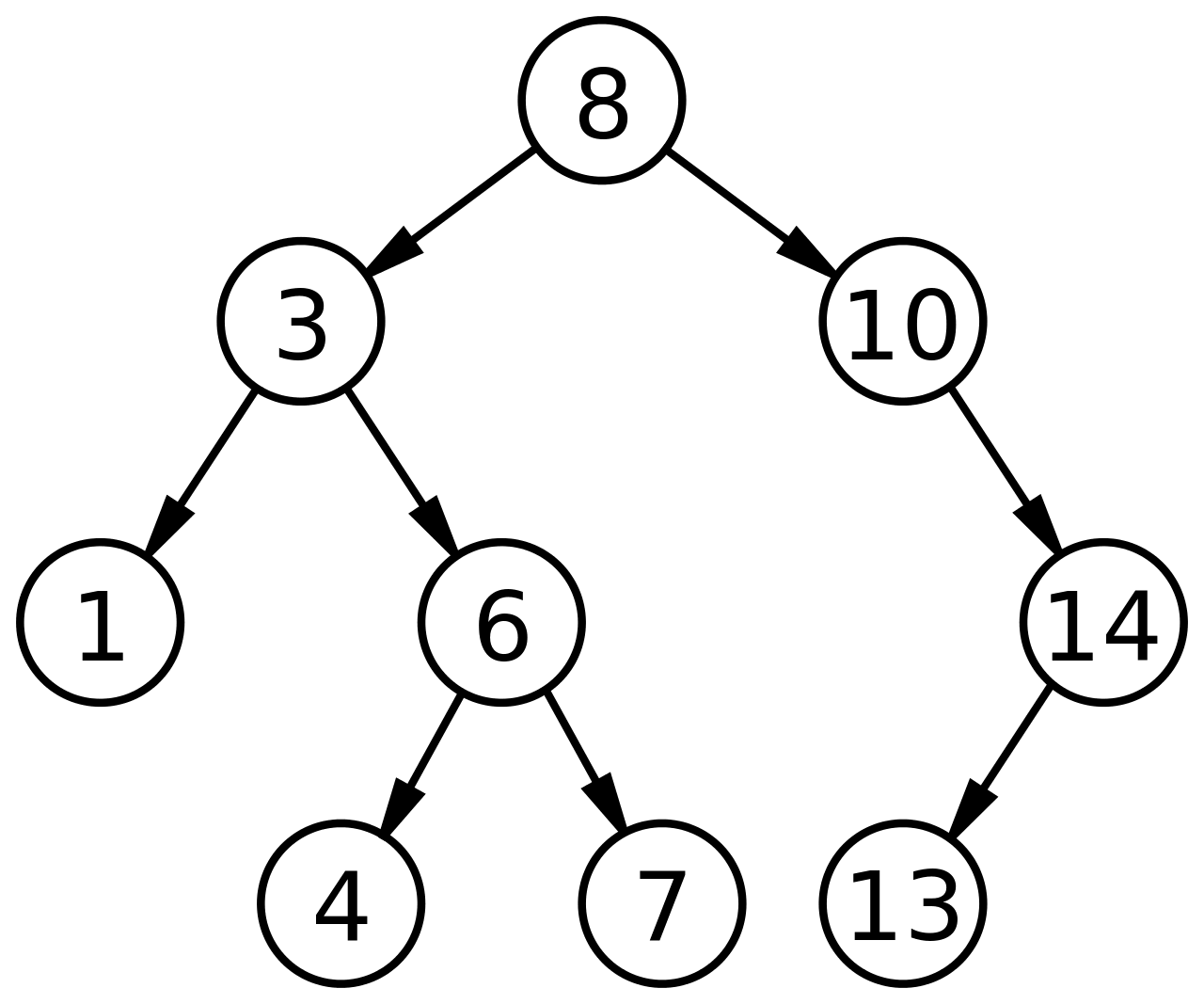
二叉搜索树及其遍历
排序类型
- 前序遍历(根节点 > 左子树 > 右子树):8 => 3 => 1 => 6 => 4 => 7 => 10 => 14 => 13
- 中序遍历(左子树 > 根节点 > 右子树):1 => 3 => 4 => 6 => 7 => 8 => 10 => 13 => 14
- 后序遍历(左子树 > 右子树 > 根节点):1 => 4 => 7 => 6 => 3 => 13 => 14 => 10 => 8
- 层次遍历(从上往下一层层来):8 => 3 => 10 => 1 => 6 => 14 => 4 => 7 => 13
二叉树的构造
javascript
// 节点对象的构造函数
function Node(data, left, right) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
Node.prototype.getData = function () {
return this.data;
};
// 二叉搜索树的构造函数
function BST() {
this.root = null;
}
// 插入方法
BST.prototype.insert = function (data) {
const n = new Node(data, null, null);
if (this.root === null) {
this.root = n;
return;
}
let current = this.root;
let parent;
while (true) {
parent = current;
if (data < current.data) {
current = current.left;
if (current === null) {
parent.left = n;
break;
}
} else {
current = current.right;
if (current === null) {
parent.right = n;
break;
}
}
}
};
const nums = new BST();
nums.insert(8);
nums.insert(3);
nums.insert(10);
nums.insert(1);
nums.insert(6);
nums.insert(14);
nums.insert(4);
nums.insert(7);
nums.insert(13);1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
前/中/后序遍历的递归实现
这个算法很好实现:
javascript
// 前序遍历二叉树
BST.prototype.preOrder = function (node) {
if (node !== null) {
console.log(node.getData());
this.preOrder(node.left);
this.preOrder(node.right);
}
};
// 中序遍历二叉树
BST.prototype.inOrder = function (node) {
if (node !== null) {
this.inOrder(node.left);
console.log(node.getData());
this.inOrder(node.right);
}
};
// 后序遍历二叉树
BST.prototype.postOrder = function (node) {
if (node !== null) {
this.postOrder(node.left);
this.postOrder(node.right);
console.log(node.getData());
}
};
// 测试
nums.inOrder(nums.root);
// 依次输出如下内容:
// 1 3 4 6 7 8 10 13 141
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
前序遍历的非递归实现
根据前序遍历访问的顺序,优先访问根结点,然后再分别访问左孩子和右孩子。 即对于任一结点,其可看做是根结点,因此可以直接访问,访问完之后,若其左孩子不为空, 按相同规则访问它的左子树;访问其左子树后,再访问它的右子树。因此其处理过程如下:
对于任一结点P:
访问结点P,并将结点P入栈;
判断结点P的左孩子是否为空,
- 若为空,则取栈顶结点并进行出栈操作,并将栈顶结点的右孩子置为当前的结点P,循环至1;
- 若不为空,则将P的左孩子置为当前的结点P;
- 直到P为NULL并且栈为空,则遍历结束。
javascript
function preOrder(bst) {
let p = bst.root;
const arr = [];
while (p !== null || arr.length > 0) {
while (p !== null) {
console.log(p.getData());
arr.push(p);
p = p.left;
}
if (arr.length > 0) {
p = arr.pop();
p = p.right;
}
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
中序遍历的非递归实现
根据中序遍历的顺序,对于任一结点,优先访问其左孩子,而左孩子结点又可以看做一根结点, 然后继续访问其左孩子结点,直到遇到左孩子结点为空的结点才进行访问, 然后按相同的规则访问其右子树。因此其处理过程如下:
对于任一结点P,
若其左孩子不为空,则将P入栈并将P的左孩子置为当前的P,然后对当前结点P再进行相同的处理;
若其左孩子为空,则取栈顶元素并进行出栈操作,访问该栈顶结点,然后将当前的P置为栈顶结点的右孩子;
直到P为NULL并且栈为空则遍历结束。
javascript
function inOrder(bst) {
let p = bst.root;
const arr = [];
while (p !== null || arr.length > 0) {
while (p !== null) {
arr.push(p);
p = p.left;
}
if (arr.length > 0) {
p = arr.pop();
console.log(p.getData());
p = p.right;
}
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
后序遍历的非递归实现
后续遍历比前中/序遍历是要麻烦一些的。
遍历顺序:左右根。左路的遍历和上面的思路是类似的,区别是元素出栈时不能直接打印, 因为如果有没访问过右侧子树的话,需要先访问右侧子树。 右侧子树访问结束后才访问根节点。
javascript
function postOrder(bst) {
let p = bst.root;
let last = null;
const arr = [];
while (p !== null || arr.length > 0) {
while (p !== null) {
arr.push(p);
p = p.left;
}
if (arr.length > 0) {
p = arr[arr.length - 1]; // 栈顶元素
// 当p不存在右子树或右子树已被访问过的话,直接访问当前节点数据
if (!p.right || p.right === last) {
p = arr.pop();
console.log(p.getData());
last = p; // 记录上一次访问过的节点
p = null; // 这个容易漏掉,避免下个循环继续访问左子树
} else {
p = p.right;
}
}
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
层次遍历
递归方案
javascript
// 遍历到某个节点后,将该节点的值推入到指定深度对应的数组中
function level(node, idx, arr) {
if (arr.length < idx) {
arr.push([]);
}
arr[idx - 1].push(node.value);
if (node.left !== null) {
level(node.left, idx + 1, arr);
}
if (node.right !== null) {
level(node.right, idx + 1, arr);
}
}
function levelOrder(root) {
if (root === null) {
return [];
}
const arr = [];
level(root, 1, arr);
return arr;
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
非递归方案
使用队列实现。
javascript
function levelOrder(root) {
const arr = [];
if (root === null) {
return arr;
}
const queue = [root];
while (queue.length > 0) {
const currentLevel = [];
const currentLevelLength = queue.length;
for (let i = 0; i <= currentLevelLength; i++) {
const node = queue.pop();
currentLevel.push(node.value);
if (node.left !== null) {
queue.push(node.left);
}
if (node.right !== null) {
queue.push(node.right);
}
}
arr.push(currentLevel);
}
return arr;
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27